
Includes translations, reflection and rotations., IMAGE : The resulting figure of a transformation, TRANSFORMATION : A geometric figure is a function that results in a change in the position, shape or size of the figure, TRANSLATION : A rigid transformation that maps all points of the same distance in the same direction. Example: Dilation, RIGID MOTION : A transformation that preserves distance and angle measures. This differs from non-rigid motion, like a dilation, where the size of the object can increase or decrease. QUESTIONS LIST: CENTER OF ROTATION : The point in which a plane figure rotates., LINE OF REFLECTION : The line that you reflect a figure across, REFLECTION : A figure across the line, These are referred to as mirror images., NON RIGID MOTION : Transformation changes the size of the pre-image. Rigid motion is otherwise known as a rigid transformation and occurs when a point or object is moved, but the size and shape remain the same. PRE IMAGE : In a transformation, the original figure A rigid motion of the Euclidean plane is a transformation f(P)f(P) of the. Use geometric descriptions of rigid motions to transform figures and to predict the effect of a given rigid motion on a given figure given two figures. Translations, Rotations and Reflections are the three basic rigid transformations in.
#Rigid motion transformation how to
ROTATION : A transformation that revolves around a point, also called a spin. 119Ju Geometry Rigid Motion Transformation How to Translation rotation. explainWhat 3 transformations are considered rigid motion - Quora. PRIME NOTATION : Symbol ('), is used to represent a transformed figure of the original figure. Often referred to as a slide or glides.ĭILATION : A transformation in which a figure is enlarged or reduced with respect to a fixed point.ĮNLARGEMENT : A dilation with a scale factor greater than 1. One major issue in 3D CA tree reconstruction is the latent motion in acquired angiograms from different views. 2.2 Rigid Motion Estimation in Object-Domain. TRANSLATION : A rigid transformation that maps all points of the same distance in the same direction. Hence, it suffices to say that, after rigid transformation, 2D projection of a 3D object remain equal if the source and projection plane are modified using the same rigid transformation. TRANSFORMATION : A geometric figure is a function that results in a change in the position, shape or size of the figure IMAGE : The resulting figure of a transformation Includes translations, reflection and rotations.
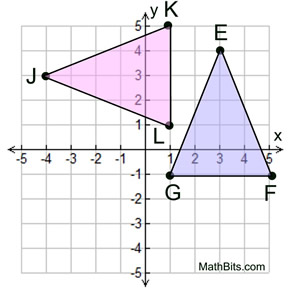
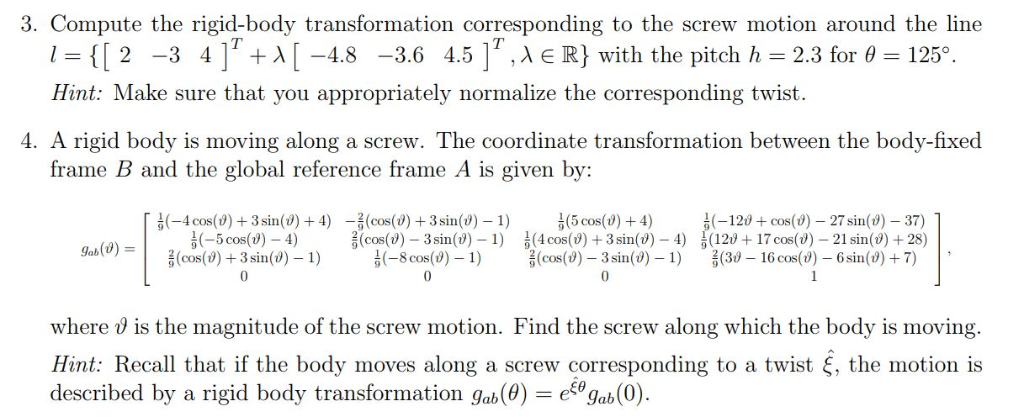
RIGID MOTION : A transformation that preserves distance and angle measures. NON RIGID MOTION : Transformation changes the size of the pre-image. REFLECTION : A figure across the line, These are referred to as mirror images. LINE OF REFLECTION : The line that you reflect a figure across CENTER OF ROTATION : The point in which a plane figure rotates.
#Rigid motion transformation pdf
PDF will include puzzle sheet and the answer key.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
